Gum Recession
Bring Life Back to Your Smile with the Best Periodontists and Modern Technology!
A Breakthrough Treatment for Gum Recession
Correct Gum Recession with AMAZING Results!

Have you noticed that you have lost some gum tissues? It is not your imagination. Receding gums (gingival recession) is an unfortunate symptom of periodontal disease and can be the result of many other factors and traumas such as crooked teeth, bruxism, or overly aggressive tooth brushing. While restoring your receding gums may not strike you as critical to your health, your gums do provide you with a barrier to infection and decay that should be repaired by gum grafting as soon as possible for optimal oral and overall health. Gum grafting will cover the exposed roots to protect them from decay, help reduce tooth sensitivity, and improve the aesthetics of your smile. Whether you have a gum graft to improve function or aesthetics, you’ll probably receive the benefits of a beautiful new smile and improved periodontal health.
Don’t let your gum recede while it can be prevented. Protect and preserve your natural teeth and your overall health with conservative dental approaches. When significant gum recession is a problem and reaches the mucosa, gum reconstruction using grafting techniques at Aria Dental with our board-certified periodontists is your best option to achieve your new beautiful smile. We invite you to call us at (949) 364-9600 or email Aria Dental to book your consultation appointment.
Gum Recession Overview
Symptoms of Gum Recession
- Sensitivity to Hot or Cold Temperatures, Sweet, Spicy, or Sour Foods.
- Your Teeth Appear Longer than Normal.
- Spaces Between Your Teeth Seem To Grow.
- The Roots of Your Teeth Begin To Show.
- A Gap or Pocket Near Gum Line
- Loose Teeth
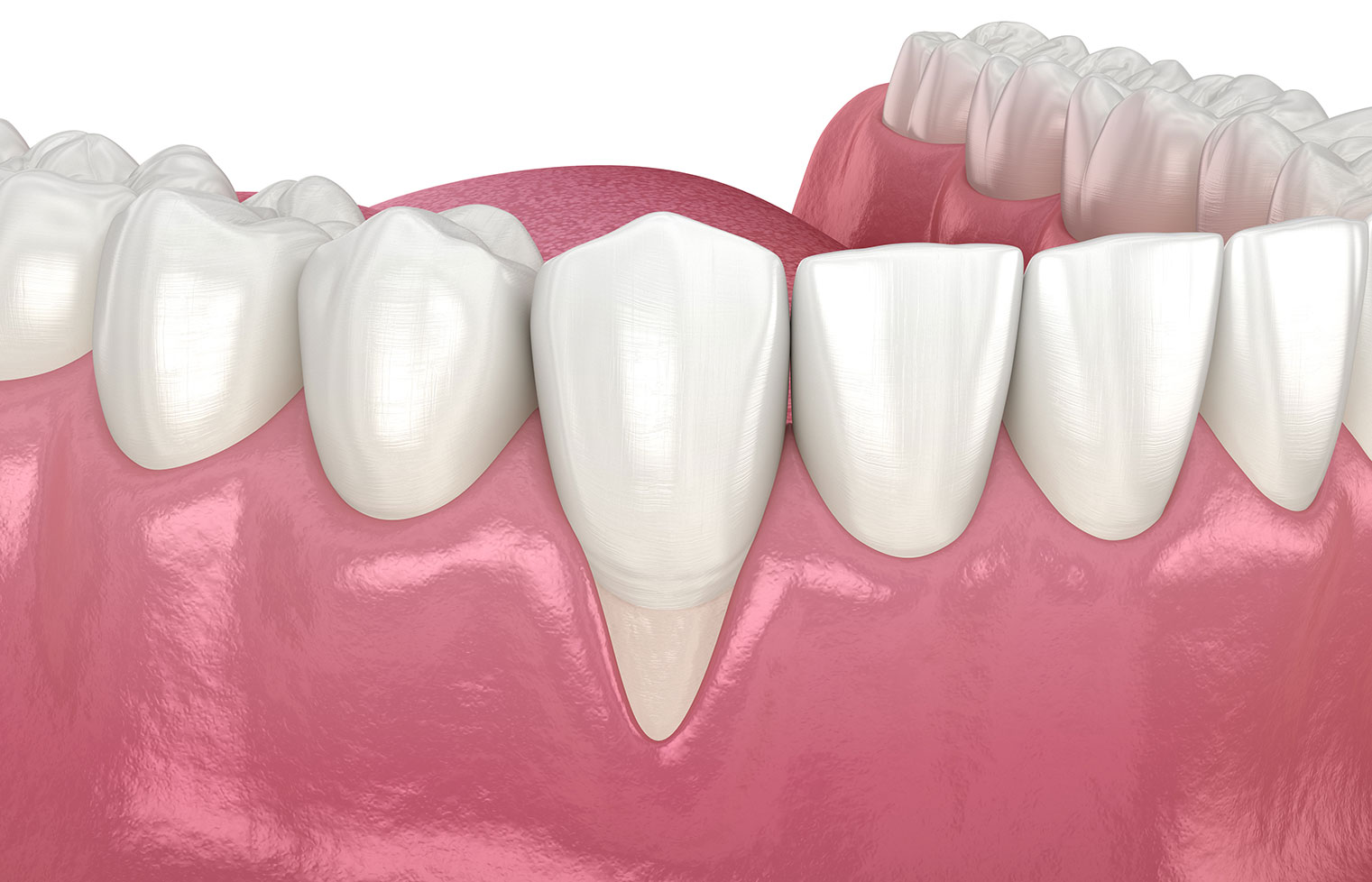

Two Main Reasons for Gum Recession
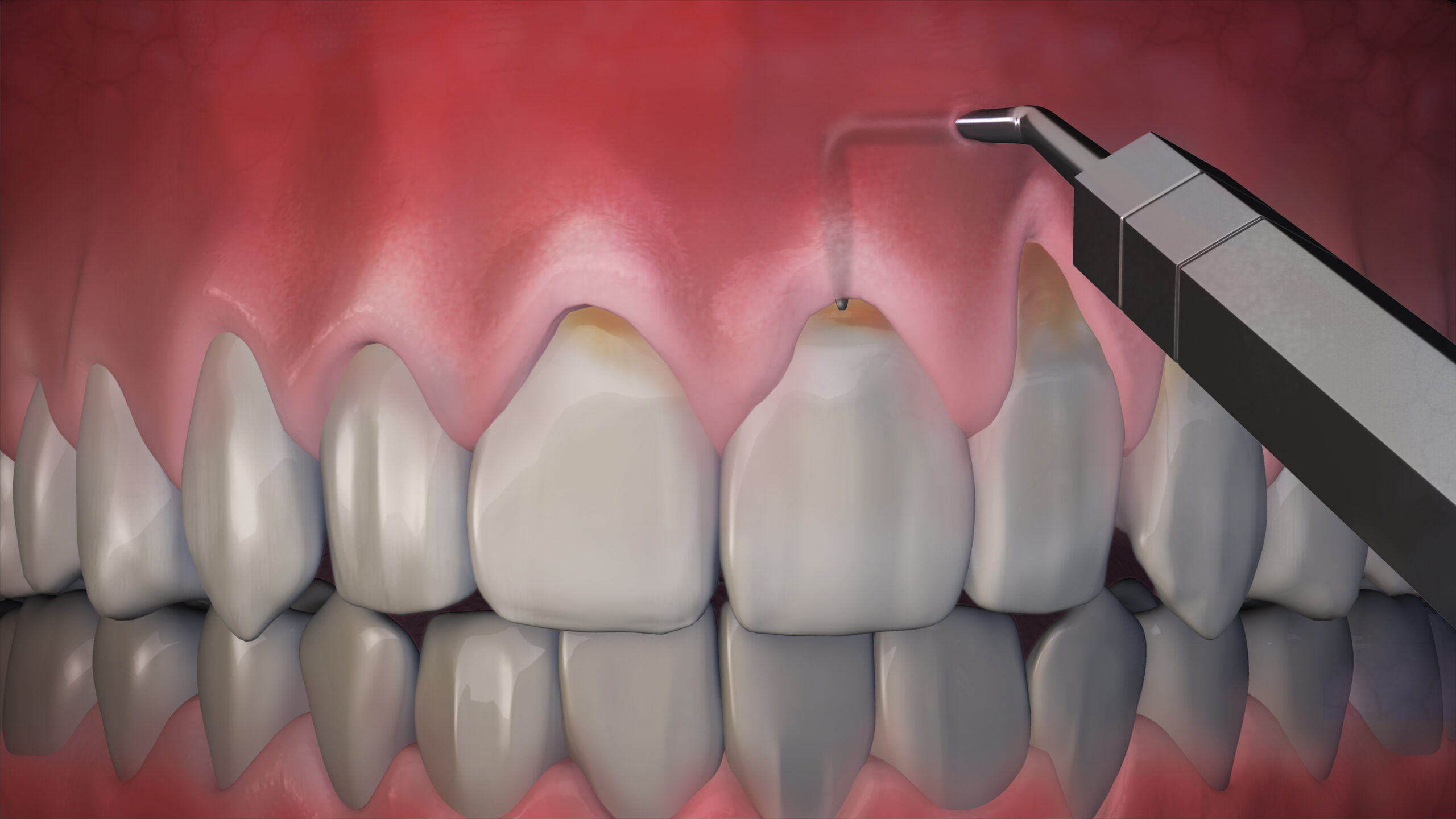
The most common cause of gum recession is a bacterial infection called periodontal (gum) disease that most often arises from poor hygiene which led to the formation of plaque (a thin film of bacteria). The plaque, calculus, or tartar buildup causes the gum to pull away from the teeth.
Plaque-Induced Gum Recession
The most common cause of gum recession is plaque-induced (bacterial infection) gum recession which arises from poor hygiene and leads to the formation of plaque (a thin film bacteria) and ultimately periodontal (gum) disease. Since gum disease is mostly a silent and chronic condition with no pain, most patients are not aware of it until it cosmetically becomes obvious or in some cases causes sensitive teeth.
When gingivitis goes untreated, gum disease will cause gums to pull away from the teeth, leaving deep pockets and gums to shrink back from the teeth, making the teeth look longer.
Non-Plaque-Induced Gum Recession
The non-plaque induce gum recession is caused by other factors rather than plaque, tartar, calculus, or infection in gum tissues. The non-plaque-induced gum recession is linked to:, ,
- Overall Health: Malnutrition or Imbalanced Hormones
- Mechanical Forces: Aggressive Brushing, Trauma, Malocclusion (Bad Bite), Misaligned Teeth & Lips or Tongue Piercing
- Bad Habits: Smoking or Chewing Tobacco
- Genetics, Shape of Teeth & Aging
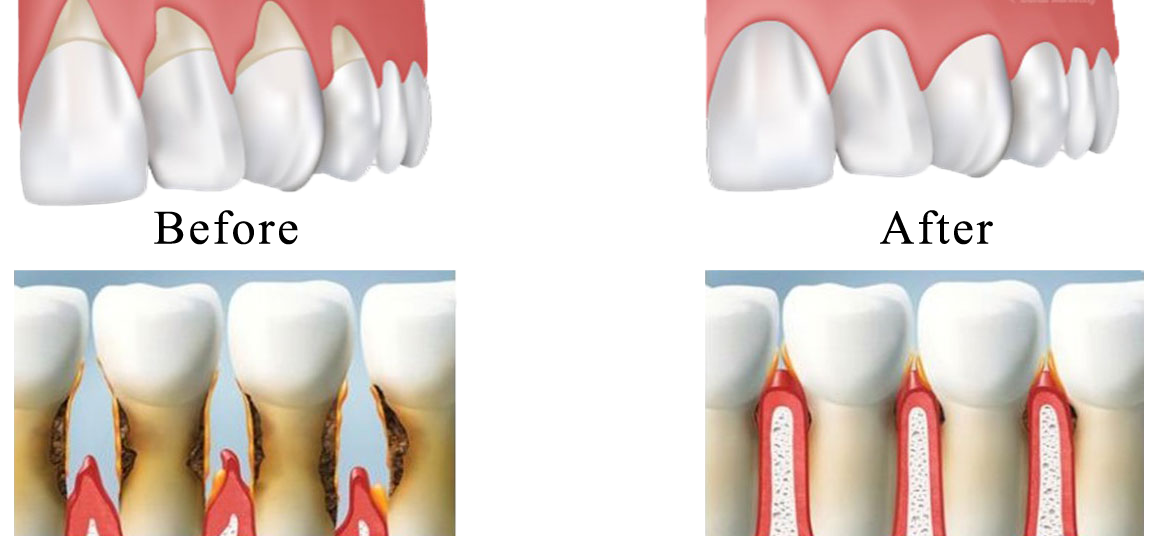
Common Reasons for Gum Recession
Inside your mouth, gum tissue forms a barrier that resists the vigorous mechanical (and microbial) effects of eating, chewing, and biting. Gums may begin to recede or shrink down, for several reasons.
The most common cause of gum recession is a bacterial infection called periodontal (gum) disease that most often arises from poor hygiene which led to the formation of plaque (a thin film of bacteria). The plaque, calculus, or tartar buildup causes the gum to pull away from the teeth.
The thickness of your gum tissues is a genetic trait you inherit from your parents. People born with thinner gums tend to be more susceptible to recession through toothbrush abrasion, wear, or injury. If you have thinner tissues, you’ll need to be diligent about oral hygiene and dental visits and pay close attention to your gum health.
Teeth normally erupt from the center of a bony housing that protects the root. If a tooth erupts or moves outside of this housing, it can expose the root and cause little to no gum tissue around the tooth. Moving the tooth orthodontically to its proper position could help thicken gum tissue and make them more resistant to recession.
While hard scrubbing may work with other cleaning activities, it’s the wrong approach for cleaning teeth. Too much force applied while brushing can eventually result in gum damage that leads to recession and tooth wear. So, “Easy does it”: Let the gentle, mechanical action of the toothbrush bristles and toothpaste abrasives do the work of plaque removal.
Uneven bites sometimes can cause gum recession. As you chew, talk, or bite, your lower moves in relation to the upper jaw, but your jawbone sits in a certain position. As your jaw closes, if one of your teeth hits before everything else, this tooth causes the lower jaw to slide in a different position. This causes a sideway force in the teeth which is unfavorable to teeth.
Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove and can cause gum recession.
Collagen strengthens the gum and promotes the binding of our teeth. As our body produces less collagen due to aging, the gum could lose its elasticity and ultimately recede. This type of gum recession develops unusual dark holes at the corners of the teeth and creates a hollow look.
Fluctuations in female hormone levels during a woman’s lifetime, such as in puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to gum recession.
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antibacterial mouthwash makes it easy for plaque to turn into calculus (tartar) — a hard substance that builds on and between your teeth and can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning. It can lead to a gum recession.
Before & After of Receded Gum Treatment
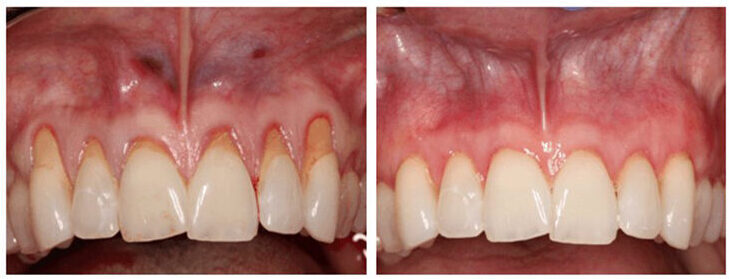
Do You Have Gum Recession?
Gum recession does not happen overnight. You may not even notice that your gums have receded, as it is a very slow, gradual process. However, without a gum tissue graft, recession can have a detrimental effect on the health and function of your teeth. If you have been diagnosed with gingivitis or periodontal disease, it is important to stop gum disease progression and maintain it.
Treatments for Gum Recessions
How Is Gum Recession Treated?
Mild gum recession may be able to be treated by your dentist by deep cleaning the affected area. During the deep cleaning, also called tooth scaling and root planing — plaque and tartar that have built up on the teeth and root surfaces below the gum line are carefully removed and the exposed root area is smoothed to make it more difficult for bacteria to attach themselves. Instead of the traditional Use of antibiotics with drug-side effects, natural and healthy ozone/oxygen can be used to get rid of any remaining harmful bacteria.
If your gum recession cannot be treated with deep cleaning because of excess loss of bone and pockets that are too deep, gum surgery may be required to repair the damage caused by gum recession.
Treatments for Gum Recession
After addressing the cause of the gingival recession, three excellent procedures can be performed by a periodontist to restore the natural symmetry of the gum and make the smile aesthetically more beautiful.
PINHOLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE™ (PST)
What Is the Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique™ (PST)?
The Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique™ is a minimally invasive option for treating gum recession. Our periodontist who is certified in Pinhole Surgical Technique uses specialized instruments to make a small hole in your gum and add collagen materials that stabilize the area of gum recession. Unlike traditional grafting techniques, this new method of PST™ is a simple, scalpel-free, and suture-free procedure. PST™ was developed and patented by John Chao, D.D.S.
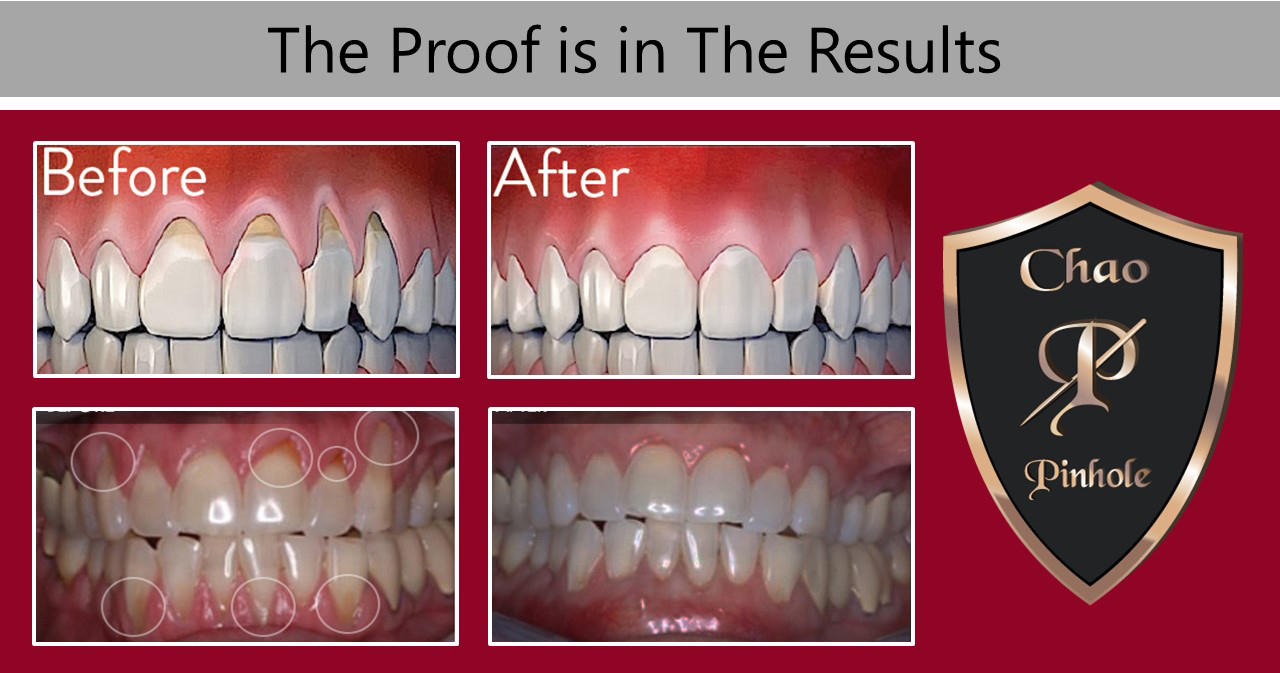
How Does the Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique Differ from Traditional Gum Grafting?
Traditional gum recession treatments involve the use of donor tissue or soft-tissue grafts to rebuild the gum line. This soft tissue would be sutured in place and would join with existing gum tissue as it healed.
While this traditional grafting treatment is effective, comparable results with better patient experience can be achieved through the Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique™.
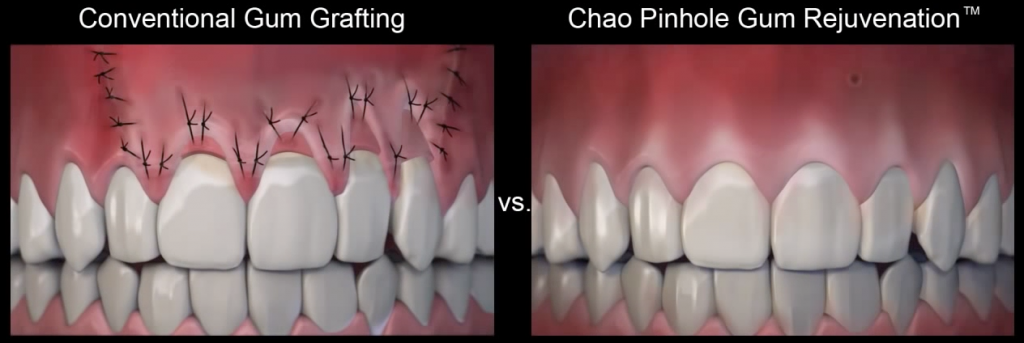
Traditional gum recession treatments involve the use of donor tissue or soft tissue grafts to rebuild the gum line. This soft tissue would be sutured in place and would join with existing gum tissue as it healed. While this traditional grafting treatment is effective, comparable results with better patient experience can be achieved through the Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique™.
BENEFITS OF PINHOLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE™
Non-Invasive
Instant Improvement
Incision and Suture-Free
No Scalpels or Blades
No Donor Tissue Needed
Excellent, Natural-Looking, Long-Lasting Results
One Visit for Multiple Areas
LANAP® (Laser-assisted New Attachment Procedure)
True Regeneration of Bone & Gum with LANAP®


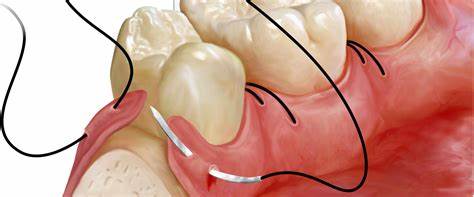
Gum Tissue Grafting Surgery
Connective Tissue Grafting (CTG)
Gingival grafts, also known as gum grafting, tissue grafting, or periodontal plastic surgery are a collective name for cosmetic periodontal surgery that is performed by an American Board-Certified Periodontics to cover unsightly, sensitive, or exposed root surfaces and to prevent future gum recession.
Tissue grafting can be done to address the receding gums and restore the tissue to a more appropriate level while halting the recession process. Tissue grafting also helps to prevent the bone loss that jeopardizes the root surface of the teeth, it is used to improve the look of your smile and to achieve an aesthetically pleasing outcome.
The gum grafting surgery is aimed to cover an exposed tooth root surface with grafted oral tissues. During this surgery, grafted gum tissues are removed from the other side of the mouth or occasionally from sterilized human donor tissue and are placed in the area of the recession. Then the area is sutured and given time to heal. Once healed, your gum will return to a healthy level that protects the underlying area and result in an improved smile.
Benefits of Gingival Grafting
Gum grafting is a common periodontal procedure. Although it sounds frightening, the procedure is commonly performed with excellent results. The major benefits are:
- Reduce Tooth Sensitivity
- Esthetic Root Coverage
- Improve Gum Health
- Prevent Root Decay
- Balance the Smile
- Prevent Further Recession & Bone Loss
Most Common Types of Gum Tissue Grafting
A gum graft also known as a gingival graft or periodontal plastic surgery is a collective name for surgical periodontal procedures that aim to cover an exposed tooth root surface with grafted oral tissue. The most common type of gum grafting is:
- Connective (Soft) Tissue Graft – This procedure is commonly used to treat and cover exposed roots. During the procedure, a flap of skin at the palate is removed for access to the tissue under the flap called subepithelial connective tissue (graft tissue). Then subepithelial connective tissue is relocated and stitched to the gum tissue surrounding the exposed root and the flap is stitched back down on the palate.
- Free Gingival Graft – This procedure is often used to thicken gum tissue. A layer of tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth (palate) instead of under the skin or another donor surface without making a flap and attached to the area affected by gum recession. This method is used mostly in people who have thin gum and need additional tissue to enlarge the gum. Both gum and graft sides will heal without any permanent damage.
- Pedicle (Lateral) Graft – This type of surgery is the preferred method for people who have enough gum tissue surrounding the exposed tooth. In this procedure, your periodontist grafts tissues from the gum around or near the affected teeth, rather than graft from the palate. During this procedure, your dentist will only partially cut away from surrounding tissue while keeping one edge attached and finally stretches the tissue over or down, covering the exposed tooth root and holding it in place with stitches.
- Acellular Dermal Matrix Allograft – This procedure is commonly used to cover exposed roots by using medically processed and donated human tissue for the graft.
Gum Grafting Procedure Pain & Recovery
The actual gum grafting procedure is painless because a local anesthetic is used to numb the affected area. A periodontist, who is a dental specialist in gum disease and the gums, typically performs this procedure.
Like any surgery, It’s completely normal to experience some discomfort or pain as you recover from a gum graft surgery; however, this will typically begin to ease as each day passes.
According to Healthline, a 2016 study investigated pain following 330 periodontal surgeries. It found that:
- Mild pain was most common, being reported 70.3 percent of the time. Moderate to severe pain was reported 29.7 percent of the time.
- The average duration of pain for gum grafting surgery was 2 days.
- Periodontal plastic surgery, which includes gum grafting, was associated with more pain than other procedures.
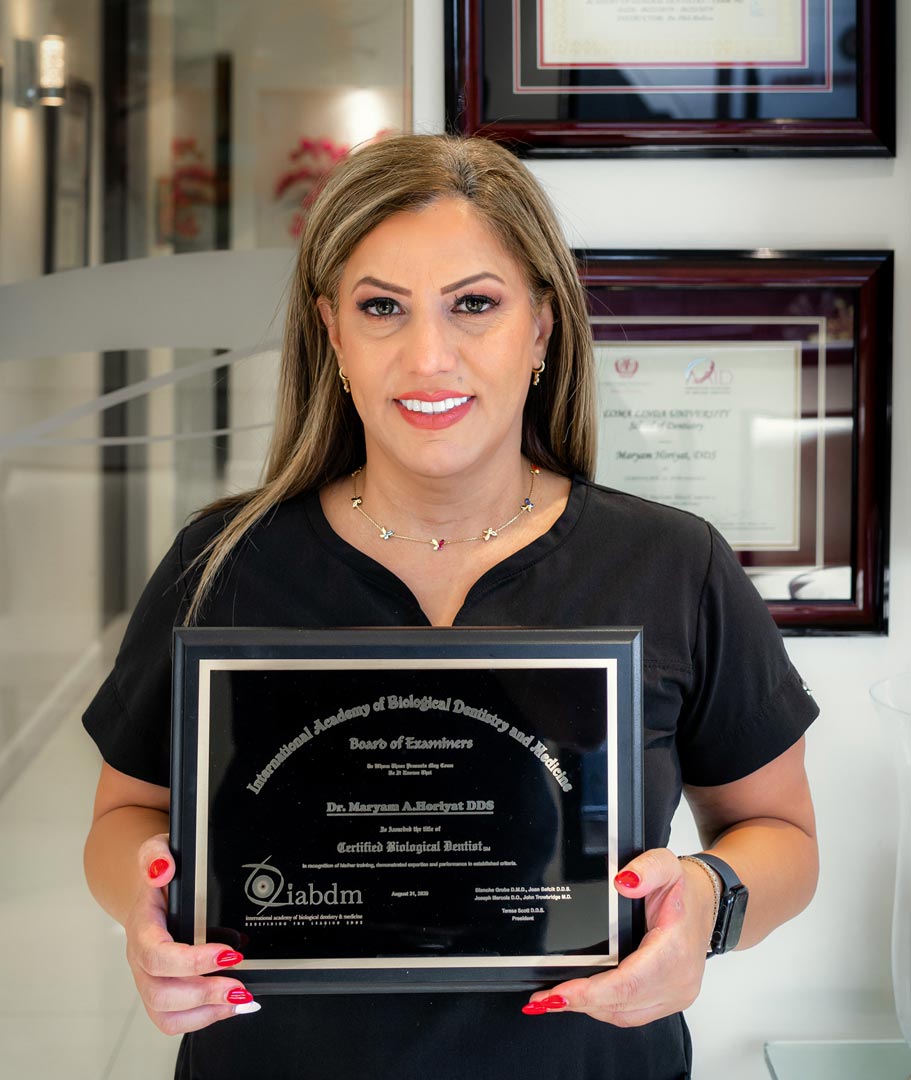
Dr. Maryam Horiyat
The Best in Modern Dentistry
PREMIER COSMETIC DENTIST IN OC WORLD-CLASS HOLISTIC DENTIST IAOMT-CERTIFIED & MEMBER IABDM CERTIFIED UCLA & UCSF GRADUATE TOP BIOLOGICAL DENTIST IN OC HI-TECH LASER DENTISTRY



Expert, Friendly & Caring
Reasons to Trust Us!


- Our Elite & Certified Biological Dentist with Advanced Training & Experience
- Our Exceptional Periodontist & Oral Surgeon
- Our Outstanding Success Rate & Life-Changing Stories
- Our Holistic, Biological, and Biomimetic Approaches
- Our Personal Attention & Highest Standards
- Our Safe Materials from Highly Reputable Companies
- Our Comfortable Sedation Options
- Our Modern and Innovative Technology