Cavities are the most common dental problem we all have dealt with in a certain period of our lives. However, knowing what a cavity is and how to prevent it saves everybody a trip to the dentist. This article will answer many cavity-related questions, including: what is a cavity? How is it treated? How can it be prevented?
The First Question: What Is a Cavity?
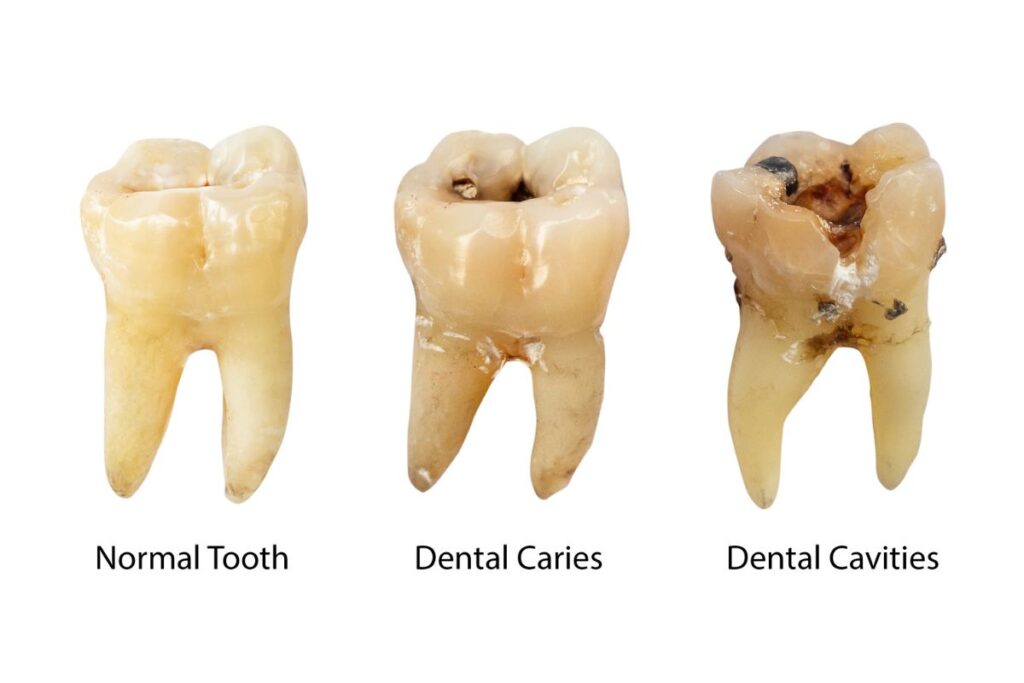
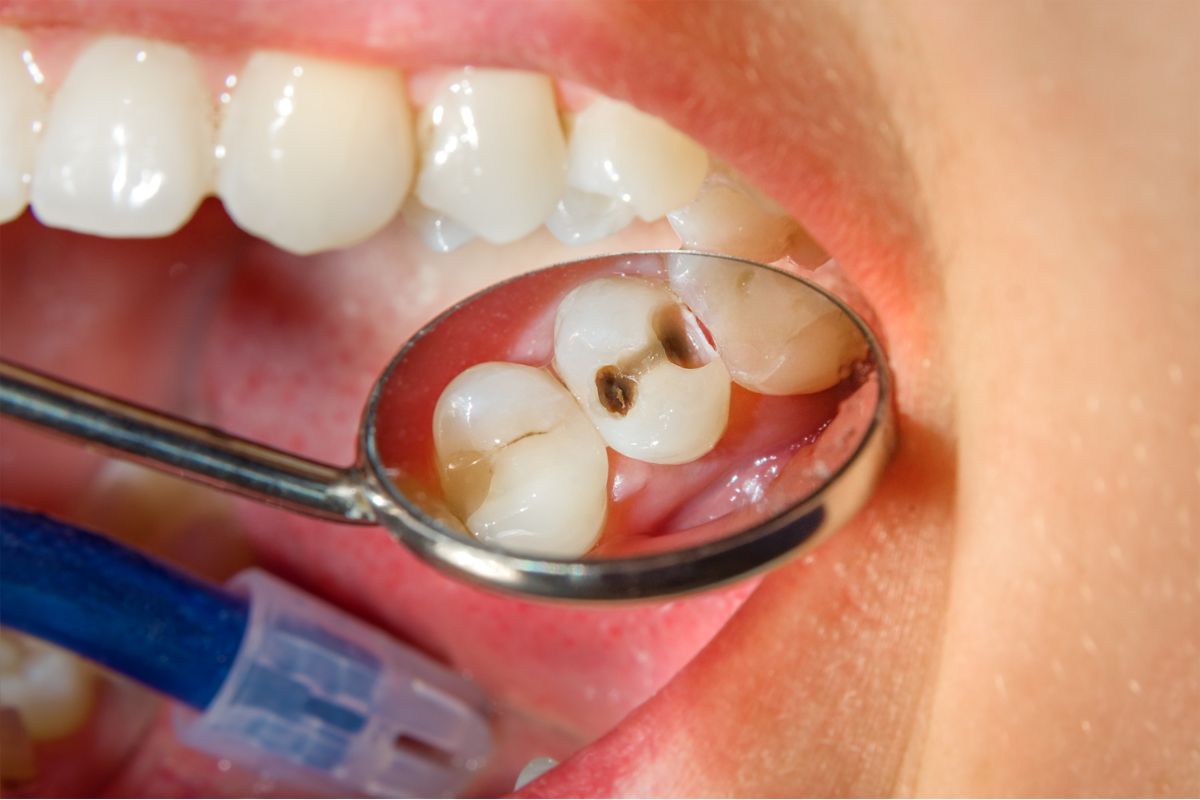
According to Mayo Clinic, “Cavities are areas in the hard surface of your teeth that are damaged.” Simply put, a cavity is a hole in your teeth caused by tooth decay. When sugary and acidic food erodes your teeth’s enamel, a cavity develops. But don’t feel bad if you have cavities.
Research has shown that over 80% of Americans have at least one cavity in their mouth in their 30s. It can happen to anyone at any age, but children are more at risk of developing cavities since they eat more sugar and brush their teeth more reluctantly. What Is a Cavity: All You Need to Know About Cavities From A to Z
The Second Question: What Causes a Cavity?
Tooth decay causes cavities in teeth; it is a long and slow process. If you want to know about cavities, you should know about tooth decay and how plaques create it. So, here is how tooth decay is formed:
Plaque Formation
When your diet contains sugar and starches that are not properly cleaned, bacteria in your mouth immediately start feeding on them. As a result, a plaque is formed, which is a transparent sticky film on your teeth. These plaques can get hardened around the gum line and turn into tartar (calculus).
Enamel Erosion
When plaque is formed, the acid in them erodes the enamel, causing tiny openings in the tooth. If it is not stopped, the acid produced by the bacteria reaches the layers under the enamel until it gets to the nerves and root.
Pulp Infection
As bacteria get to the pulp, this layer gets irritated and swollen, which presses nerves and causes toothache. If left untreated, the swelling might even affect your face. So, never let tooth decay get this severe. The more severe it gets, the harder it is to treat.
The Third Question: What Are the Types of Cavity?
Cavities are sometimes categorized based on the part of the teeth they develop in. Here are three common types of cavities:
Surface
These types of cavities are the slowest in the development. Many people in their 20s experience a cavity between teeth, which can be easily prevented by following a proper oral routine.
Pit and Fissure
The cavity can also develop on the top of your teeth (the part you use for chewing). Teenagers mostly experience this type of cavity, and their parents should know it gets bigger quickly. So, it would be best if you didn’t hesitate to treat it.
Root
People with receding gums are more in danger of root decay than other adults. When there is receding gum, dental plaques get to the root of your teeth, which is harder to treat and prevent. So, generally, all holistic dentists recommend you treat a receding gum as soon as possible.
The Fourth Question: What Are the Stages of a Cavity?
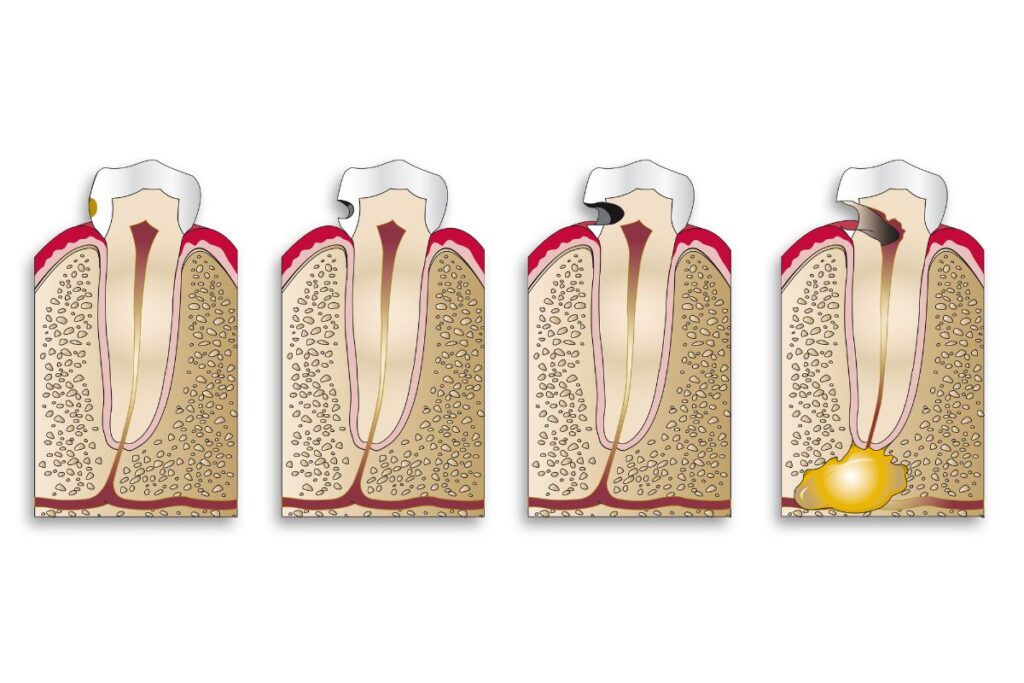
As we mentioned, decay is the root cause of a cavity, and if you want to know the stages of a cavity, you should look for decay. The five stages of tooth decay are:
Demineralization
In the first stage, small and white spots appear on your tooth. This means that the tooth’s enamel is losing minerals. That is why this stage is called demineralization (or breakdown of minerals).
Enamel Decay
If you overlook demineralization, the decay is going to break your enamel. Now, you can see visible holes in the site of decay. Those white spots turn brownish in this stage of decay.
Dentin Decay
Under the tooth enamel, there is a layer called dentin. It is not as hard as the enamel, and cavities in teeth can move much faster through this layer. When you have dentin decay, you can feel sensitivity to hot and cold foods and beverages. Those spots on your teeth might also turn darker brown.
Pulp Damage
The pulp is the last layer that contains nerves and vessels. When tooth decay gets to the pulp, you may feel pain in your teeth and redness in the gum around them. Those spots on your teeth turn dark brown or black at this stage.
Abscessed Tooth
The deep cavity through the pulp can get infectious. As a result, pockets of pus are formed near the tooth root. An abscessed tooth causes pain and facial swelling, but that is not the worst part. It can spread to other parts of your body as well.
The Fifth Question: What Are the Risk Factors for a Cavity?
Everybody can get a cavity, but the following factors significantly affect the likelihood of having one:
Age
Young children and teenagers are at a higher risk of getting cavities in the United States. However, there is a risk for older adults too. As we age, our teeth wear down, and gums might recede. On top of this, adults might take medications that cause dry mouth and lead to a cavity.
Diet
If you are a fan of sticky or acidic foods and drinks, the chance of getting a cavity is pretty high. You should eat less ice cream, honey, sugar, soda, cookies, and candy bars if you want to reduce the risk of multiple cavities in your teeth.
Snacking
If you are one of those people who need to snack on something constantly, there is bad news. Eating and drinking throughout the day encourages the bacteria in your mouth to produce more acid. Thus, your teeth will be worn out sooner.
Bedtime Feeding
Baby bottle tooth decay happens when you put your baby in bed with a bottle of milk or sugary liquids. Since these beverages stay on the teeth the whole night, they cause cavities. It is therefore recommended not to feed your baby before bedtime.
Bad Brushing
Cleaning your teeth plays a big part in preventing cavities. Proper brushing stops plaque formation, preventing the cavity at its root. Talk to your holistic dentist and ensure your brushing technique is correct and effective.
Worn Fillings
Your cavity fillings weaken and break down after several years. Then plaques can quickly build up on the worn-out fillings and cause decay underneath the teeth.
Dry Mouth
Your saliva helps you with oral hygiene by washing away food and plaques and countering the acid produced by the bacteria. If you have a medical condition that might cause dry mouth, talk to your holistic dentist to ensure it won’t cause cavities.
GERD
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) causes stomach acid to go up into your mouth and damage your teeth. Your dentist will tell you how to improve GERD and if your stomach acid is causing cavities.
Eating Disorders
Anorexia and bulimia are terrible for your teeth, as stomach acid and vomit wash away the enamel of your teeth. These disorders also affect saliva production and might cause a dry mouth, one of the more prominent factors in forming a cavity.
The Sixth Question: How Can You Prevent a Cavity?

Like any other oral complication, maintaining proper and effective oral hygiene is the best way to prevent a cavity. Here are some tips you might find helpful:
- – Choose a soft toothbrush and clean your teeth twice a day;
- – Reduce sugary and acidic food and beverages;
- – Don’t forget to floss at least once a day to clean plaque between your teeth;
- – Schedule at least two appointments with your dentist every year.
The Seventh Question: What Are the Symptoms of a Cavity?
Symptoms of a cavity depend on its type and the stage. At the very early stages, you might not even have any symptoms. That’s just one reason to visit your dentist regularly. At later stages, signs of a cavity include:
- – Bad breath;
- – Bleeding gums;
- – Sudden tooth pain that has no apparent cause;
- – Tooth sensitivity;
- – Pain as you bite down;
- – Facial swelling;
- – Sharp pain while consuming hot or cold food and beverages;
- – Visible holes;
- – Staining.
The Eighth Question: How Is a Cavity Diagnosed?
Regular checkups by a holistic doctor are the best way to diagnose early cavities. If you can see a cavity, it’s grown very large. Your dentist can only see cavities beneath the teeth with X-rays. Therefore, please don’t wait until it’s visible.
The Ninth Question: How Is a Cavity Treated?
A cavity can be treated based on the severity of the damage to the tooth. Here are three of the most common treatments for a cavity:
Dental Filling
If there is a hole in one of your teeth, your dentist removes the decayed part and fills the hole to stop further damage. Remember to ask for biocompatible materials instead of amalgam filling as amalgam fillings contain toxic metals such as mercury.
Root Canal
A root canal is a widespread solution for cavities. However, holistic doctors prefer alternative treatments since there are still dead tissues in the tooth socket after the treatment is over. These tissues can quickly get infected and further complicate your oral health.
Tooth Extraction
Tooth extraction is recommended for severe cavities or as an alternative to root canals. It is considered a holistic solution since there are no dead tissues in your mouth, and you can replace the tooth with a zirconia implant, which is safe and durable.
The Tenth Question: Where to Find a Holistic Dentist for a Cavity
Hopefully, this article has answered all of your questions. If, however, you are looking for a holistic dentist in California to ensure your cavity treatment is safe and natural, Aria Dental in Orange County is your ideal option. Feel free to contact us for a consultation so our professional team can address your every concern, including cavities.